QML 可以使用x, y属性手动布局元素,但这些属性是与元素父对象左上角位置紧密联系的,不容易确定各子元素的相对位置。为此,QML提供了定位器和锚点来简化元素的布局。
定位器(Positioner)
定位器是一种容器元素,专门用来管理界面中的其他元素,与传统的 Qt Widgets 中的布局管理器类似。使用定位器,你可以很方便地把众多的元素组织在一起,形成非常规则的界面效果。定位器包括 Row(行定位器)、Column(列定位器)、Grid(表格定位器)、Flow(流式定位器)。
不过有一点需要的是,定位器不会改变它管理的元素的大小,与你使用 Qt Widgets 中的布局管理器的经验不同,不过如果你希望使用 “自动根据界面尺寸变化调整孩子们的尺寸” 这种特性,可以使用 Qt Quick 中的布局管理器。
Row 行定位器
Row 沿着一行安置它的孩子们,在你需要水平放置一系列的 Item 时,它比锚布局更加方便。一旦你把一个 Item 交给 Row 来管理,那就不要再使用 Item 的 x 、 y 、 anchors 等属性了, Row 会安排得妥妥的。
在一个 Row 内的 item ,可以使用 Positioner 附加属性来获知自己在 Row 中的更多位置信息。 Positioner 有 index 、 isFirstItem 、 isLastItem 三个属性。
1 | import QtQuick 2.0 |
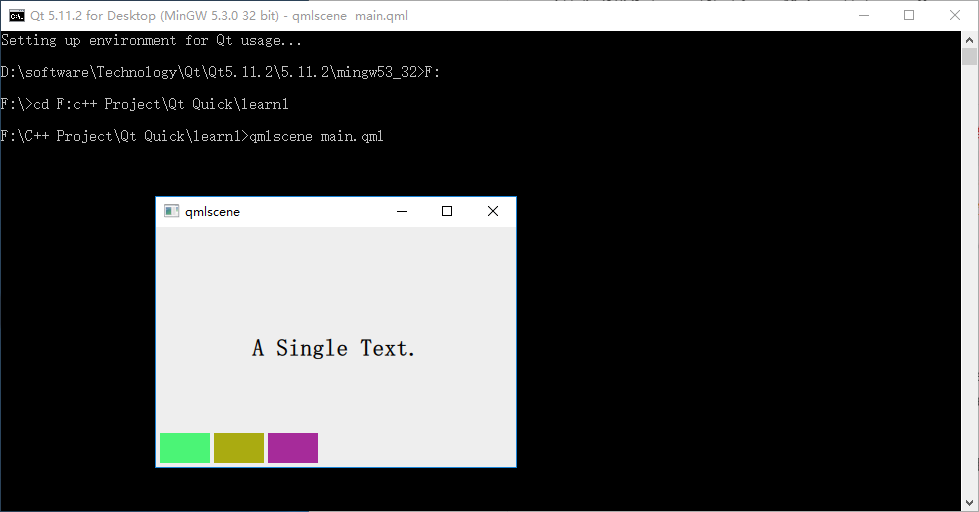
因为 Row 本身是一个 Item ,所以你可以使用锚布局来定位一个 Row ,示例中这么做了,把 Row 放在界面的左下角。
Row 有一个 spacing 属性,用来指定它管理的 Item 之间的间隔。还有一个 layoutDirection 属性,可以指定布局方向,取值为 Qt.LeftToRight 时从左到右放置 Item ,这是默认行为,取值为 Qt.RightToLeft 时从右向左放置 Item 。还有其它的一些属性,请参看 Qt SDK。
Column 列定位器
Column 与 Row 类似,不过是在垂直方向上安排它的子 Items 。Column 本身也是一个 Item ,可以使用 anchors 布局来决定它在父 Item 中的位置。 Column 的 spacing 属性描述子 Item 之间的间隔。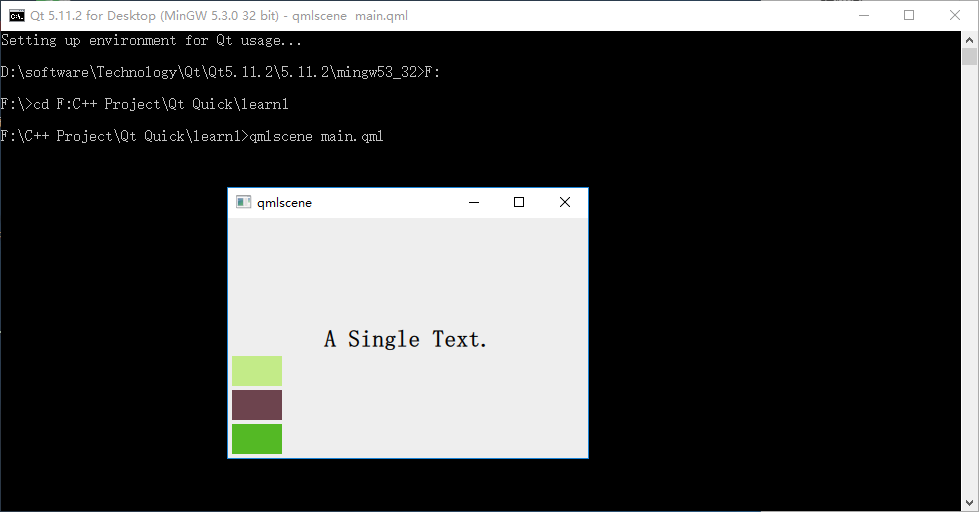
Grid 表格定位器
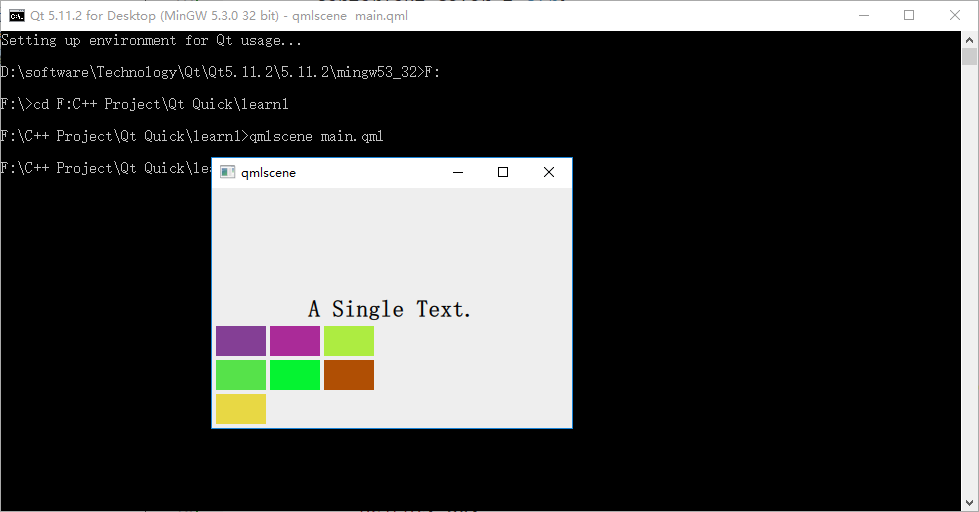
Grid 在一个网格上安置它的子 Items ,它会创建一个拥有很多单元格的网格,足够容纳它所有的子 Items 。Grid 会从左到右、从上到下把它的子 items 一个一个塞到单元格里。 item 默认会被放在一个单元格左上角 (0, 0) 的位置。
你可以通过 rows 和 columns 属性设定表格的行、列数。如果你不设置,默认只有四列,而行数则会根据实际的 item 数量自动计算。rowSpacing 和 columnSpacing 指定行、列间距,单位是像素。
Grid 的 flow 属性描述表格的流模式,可以取值 Grid.LeftToRight ,这是默认模式,从左到右一个挨一个放置 item,一行放满再放下一行;取值为 Grid.TopToBottom 时,从上到下一个挨一个放置 item,一列放满再放下一列。
horizontalItemAlignment 和 verticalItemAlignment 指定单元格对齐方式。默认的单元格对齐方式和 layoutDirection 以及 flow 有关。
1 | import QtQuick 2.0 |
Flow 流式定位器
Flow 其实和 Grid 类似,不同之处是它没有显式的行、列数,它会计算自身尺寸和子 item 尺寸来根据需要几行。
它的 flow 属性,默认取值 Flow.LeftToRight ,从左到右安排 item ,直到 Flow 本身的宽度被超出时折行;当 flow 取值 Flow.TopToBottom 时,从上到下安排 item ,直到 Flow 本身的高度被超出时开始在下一列上安排 item 。
Repeater 重复器
通常Repeater(重复元素)与定位器一起使用。它的工作方式就像for循环与迭代器的模式一样。在这个最简单的例子中,仅仅提供了一个循环的例子。
1 | DarkSquare { |
在这个重复元素的例子中,我们使用了一些新的方法。我们使用一个颜色数组定义了一组颜色属性。重复元素能够创建一连串的矩形框(16个,就像model模型中定义的那样)。每一次的循环都会创建一个矩形框作为repeater的子对象。在矩形框中,我们使用了JS数学函数Math.floor(Math.random()*3)来选择颜色。这个函数会给我们生成一个0~2的随机数,我们使用这个数在我们的颜色数组中选择颜色。注意之前我们说过JavaScript是QtQuick中的一部分,所以这些典型的库函数我们都可以使用。
一个重复元素循环时有一个index(索引)属性值。当前的循环索引(0,1,2,….15)。我们可以使用这个索引值来做一些操作,例如在我们这个例子中使用Text(文本)显示当前索引值。
布局元素
QML使用anchors(锚)对元素进行布局。anchoring(锚定)是基础元素对象的基本属性,可以被所有的可视化QML元素使用。一个anchors(锚)就像一个协议,并且比几何变化更加强大。Anchors(锚)是相对关系的表达式,你通常需要与其它元素搭配使用。
一个元素有6条锚定线(top顶,bottom底,left左,right右,horizontalCenter水平中,verticalCenter垂直中)。在文本元素(Text Element)中有一条文本的锚定基线(baseline)。每一条锚定线都有一个偏移(offset)值,在top(顶),bottom(底),left(左),right(右)的锚定线中它们也被称作边距。对于horizontalCenter(水平中)与verticalCenter(垂直中)与baseline(文本基线)中被称作偏移值。
详情参考:https://qthub.com/static/doc/qmlbook/cn/quick_starter/layout_items.html